Associations of ACEI/ARB use and patient death in the four different strategies of model selection. Variables that were identified as confounder were included into the multivariate analysis. All predicting variables with the exception of recipient age and year of first renal replacement therapy were used as time dependent covariates in the Cox regression analysis.
Screenshot of all variables in the relational database.
Visual description of events within the first three months after first transplantation.

Associations of ACEI/ARB use and graft failure in the four different approaches to model building. Variables that were identified as confounders were included into the multivariate analysis. All predicting variables with the exception of donor age, BCAR and CAN were used as time dependent covariates in the Cox regression analysis.
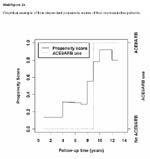
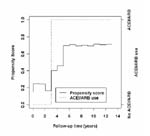
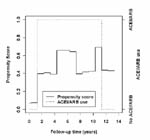
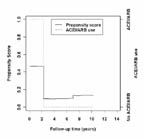
Graphical example of time dependent propensity scores of four representative patients.

Modification of the hazard ratio (HR) of ACEI/ARB use for death by potential confounding variables. Those variables that changed the HR of ACEI/ARB use by more than 10 % if omitted from a bivariable model involving ACEI/ARB use and the potential confounder were included in a ‘multivariable model adjusted for variables identified as confounders’ (see table 2 bottom).
Modification of the hazard ratio (HR) of ACEI/ARB use for graft failure by potential confounding variables. Those variables that changed the HR of ACEI/ARB use by more than 10% if omitted from a bivariable model involving ACEI/ARB use and the potential confounder were included in a ‘multivariable model adjusted for variables identified as confounders’ (see table 3 bottom).
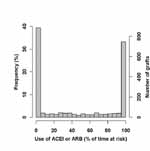
Duration of ACEI/ARB use as percentage of follow up time. The majority
of subjects either received (31.4 %) or did not receive (38.5 %) ACEI/ARB during the whole
follow up period.
The remaining 30.1 % of patients received ACEI/ARB therapy for equally
distributed variable times of follow up.
Cumulative incidence of ACEI or ARB medication over time.

Cumulative incidence of other (non-ACEI/ARB) antihypertensive drugs over time.

Scaled Schoenfeld residuals (test of proportional hazards assumption) for the patient survival model with confounding factors heart disease, vascular disease and the number of antihypertensive drugs (slope, p = 0.44).
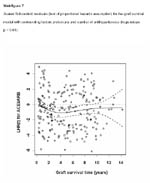
Scaled Schoenfeld residuals (test of proportional hazards assumption)
for the graft survival model with confounding factors heart disease, vascular disease, cholesterol,
hemoglobin and the number of antihypertensive drugs (slope, p = 0.68).