
Assessment of working correlation structure

Boxplot of potassium levels vs. year after engraftment, stratified for ACEI/ARB use.
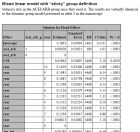
Mixed linaer model with “sticky” group definition
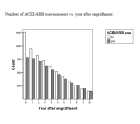
Number of ACEI/ARB user/nonusers vs. year after engraftment.

Testing for interaction between ACEI/ARB and year of use (sticky group definition)

Percentage of ACEI/ARB user/nonuser vs. year after engraftment.
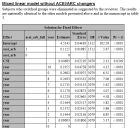
Mixed linaer model without ACEI/ARB changers.
Subjects who switched groups were eliminated as suggested by the reviewer. The results are materially identical to the other models presented above and in the manuscript in table 3.

Residual diagnostics

Test for interaction of ACEI/ARB and CNI use


a,b: Residuals against predicted values
c,d: Absolute residuals against predicted values (to detect heteroscedasticity)