TABLES
FIGURES

Characteristics of all 1,829 patients with graft survival of at least 90 days
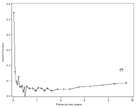
Hazard function (risk for graft loss or death per year)

Complete Case Only analysis
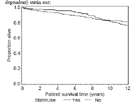
Cardiovascular death outcome
Among the 2041 patients, 223 died with confirmed cardiovascular causes. 35 of these 223 deaths occurred before day 90. Extended Kaplan-Meier plot stratified for (timedependent) statin

Analysis of sensitivity of multiple imputation approach (comparison of results from multiple imputation after randomly deleting data and non-randomly deleting data)
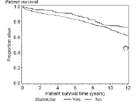


Analysis including events between days 0 and 90
Kaplan-Meier analysis
a Patient survival
b actual graft survival
c functional graft survival



Analysis repeated without cholesterol
a Patient survival
b actual graft survival
c functional graft survival

MSM analysis without statin users at baseline

Clinical expertise models (HLA mismatches, CIT, Induction therapy, donor age forced into model)



Interaction analysis (HR of statin use in subgroups which were close to significant)
a Patient survival
b actual graft survival
c functional graft survival



Assessment of proportional hazards assumption of statin use
a Patient survival
b actual graft survival
c functional graft survival
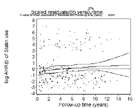
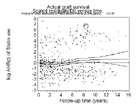
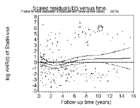
Schönfeld residuals
a Patient survival
b actual graft survival
c functional graft survival

Analysis of time to (biopsy confirmed) acute rejection
Results from Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression. Dependent variable: BCAR up to one year after transplantation.

Multivariable Cox’s proportional hazards model assessing the confounder-adjusted association of statin treatment on actual graft survival (graft failure and death with functioning graft counted as endpoints)
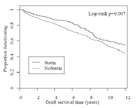
Kaplan-Meier curves of actual graft survival

Multivariable Cox analysis assessing the effect of statin treatment on patient survival and functional graft survival
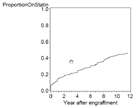
Onset of statin treatment after transplantation