Dunkler D(1-3), Dehghan M(1), Teo KK(1-4), Heinze G(3), Gao P(1), Kohl M(1-3), Clase CM(4), Mann JFE(2,5), Yusuf S(1,4), Oberbauer R(3,6)
1- Population Health Research Institute, Hamilton Health Sciences/McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
2- Universitaetsklinikum Erlangen, Department of Nephrology, Germany
3- Section of Clinical Biometrics, Center for Medical Statistics, Informatics and Intelligent Systems, Medical University of Vienna, Austria
4- McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
5- Schwabing General Hospital, and KfH Kidney Center, Munich, Germany
6- KH Elisabethinen Linz, Austria, and Department of Internal Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna, Austria

Description of food items in the Food Frequency Questionnaire. These examples are not exhaustive.
View PDF

Assumed protein content per serving size and conversion between servings and gram based on
USDA United State Department of Agriculture National Nutrient database for standard reference.
View PDF

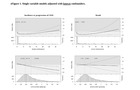
Single variable model with mAHEI adjusted with known confounders, separated for
participant’s albuminuria status at baseline.
View PDF

Changes in the number of participants with new micro- or macro-albuminuria at study end
when the minimum increase in UACR between baseline and 5 years follow-up measurement is changed.
View PDF
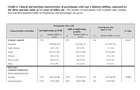
Clinical and nutrition characteristics of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus, separated by
the three outcome states at 5.5 years of follow-up-. The number of participants with available data; median,
first and third quartiles (IQR) or frequencies and percentages are given.
View PDF
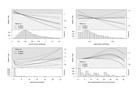
Comparison of estimates of multivariable models adjusted with known confounders after 5.5
years of follow-up (Webtable 7) and after 2 years of follow-up (Webtable 13).
View PDF

Distribution of the three outcome states at the 5.5 year follow-up status separated by normo-
and micro-albuminuria at baseline.
View PDF


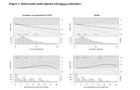
Single variable model with mAHEI and multivariable model adjusted with the extended set of confounders 1.
View PDF

Single variable model with mAHEI and multivariable model adjusted with the extended set of confounders 2.
View PDF


Single variable model with mAHEI and multivariable model adjusted with the extended set of confounders 1.
View PDF

Single variable model with mAHEI and multivariable model adjusted with the extended set of confounders 2.
View PDF

Combined Renal Outcome: Multinomial logit model including only variables from the set of known confounders.
View PDF

Combined Renal Outcome: Multinomial logit model including only variables from the set of extended confounders 1.
View PDF

Combined Renal Outcome: Multinomial logit model including only variables from the set of extended confounders 2.
View PDF









